Chances are you have heard the term “Industry 4.0” thrown around in an online form recently - or maybe you are wondering how you missed Industry 1.0 - 3.0. In either case, the term, even though sometimes seen as a buzzword, deserves our attention for a bit. In this article, we’ll clear things up around the meaning and implications of Industry 4.0. and why you should embrace it sooner rather than later.

What Is Industry 4.0?
What is industry 4.0? A simple Industry 4.0 definition is: “the fourth revolution that has occurred in manufacturing”. Some even call it the fourth Industrial Revolution. To understand the gravity of the term, we’ll need to take a trip back in time.
Originally, manufacturing was driven by water and steam (1.0), followed by assembly lines and electricity (2.0), and then by computers (3.0). Now we are moving towards a new revolution, one where manufacturing is overseen by a digitized and connected set of machines that revolutionize the entire manufacturing process.
Enter “smart factories” where machines are all connected to the web and to a system that allows “the factory” to see the whole production chain and then make its own decisions. Some are concerned that as factories become “smart,” workers will be replaced by machines. This is something that has been a concern since the dawn of the Industrial Revolution. A pre-Covid study by McKinsey found that up to 30% of jobs could be automated by 2030. In addition, new research by the firm suggests that up to 25% more workers than previously estimated may need to switch occupations due to acceleration brought on by the pandemic.
Irrespective of these concerns, the train has left the station and Industry 4.0 is upon us. Organizations need to invest now to ensure they remain competitive long term. Early adopters such as Google and Microsoft are already benefiting from increased productivity and higher profits. Experts agree that Industry 4.0 is different from the former stages of the Industrial Revolution in that those phases were linear in growth. Industry 4.0 is exponential in growth and late adopters will likely struggle for survival as competitors benefit from advanced automation and connectivity.
Most organizations know that they need to digitize their operations, better understand the needs of their customers, and be nimble enough to make changes faster than they do today. All of this requires the integration of smart machines and the implementation of the Industry 4.0 technologies as outlined in the next section of this article.
The 11 pillars of Industry 4.0
PwC provides a comprehensive Industry 4.0 framework. As you can see from the graphic below, Industry 4.0 relies on data and analytics to drive technologies that will improve productivity and drive unnecessary costs out of the manufacturing process.
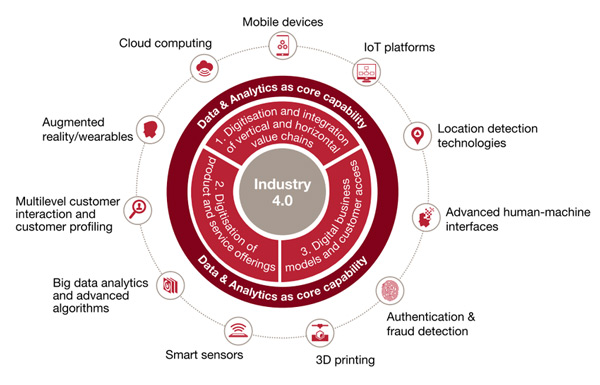
PwC’s 11 pillars of industry 4.0. are:
-
Mobile Devices
Industry 4.0 is driven by the availability of mobile. Data can be shared readily with workers and customers have access to information like never before.
-
IoT Platforms
The Internet of Things involves a system of computing devices that are interrelated, including both digital and mechanical machines that can move data over a network without requiring human interaction or even human-to-computer interaction.
-
Location Detection Technologies
This includes the use of wireless technologies to determine the location of a device or sensor.
-
Advanced Human-Machine Interfaces
These interfaces connect humans and machines and can be as simple as the use of a touch screen versus knobs and controls.
-
Authentication and Fraud Detection
This form of detection allows for the identification of an appropriate user or process and ensures that the appropriate action is authorized.
-
3D Printing
3D printing allows for the creation of a 3-dimensional object from a computer-aided design.
-
Smart Sensors
These are sensors that are applied in various areas of the manufacturing process. They provide real-time data and analytics to allow for faster adjustments that can drive profitability and increase customer satisfaction.
-
Big Data Analytics and Algorithms
This information is stored in the Cloud and can be easily accessed at any time during the manufacturing process to make real-time adjustments.
-
Multi-level Customer Interaction and Profiling
Sensors, mobile, and other customer interactions allow for access to customer data to drive real-time production and product changes.
-
Augmented Reality/Wearables
Designed to improve safety, quality and productivity, augmented reality/wearables solicit digitization to improve on what a human can do on the manufacturing line.
-
Cloud Computing
All the data retrieved during the manufacturing process must be saved somewhere where it’s easily accessible. With Cloud Computing, data is not stored on the premises or on a device, but in a data center location connected to the internet.
[globalcta id="CTA-CorpTraining-v1"]
Conclusion
As challenging and costly as it may be, organizations are realizing the need to digitize their operations and get closer to the needs of their customers. PwC estimates that 52% of companies that invest in Industry 4.0 initiatives should expect to see a return on investment within two years. If you are considering management consulting as a career, Industry 4.0 brings with it exciting challenges and opportunities. Many organizations are hiring consultants to help with strategy and implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies and processes, and that will only accelerate in the next decade. Gaining specialization in data, analytics, AI, machine learning, etc. is a smart way to prepare for the future of business – whether that’s in consulting or elsewhere. It’s an exciting time to be alive!
Additional Reading:
- Becoming Data Driven
- Data Science Case Study Interview Prep
- What Is Big Data?: How Will It Affect Consulting
- Data Analytics: Do Businesses Really Need It?
- Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide