The critical path method is a project management tool that documents the many critical steps of a project and the longest period of time that is required to successfully complete it. The critical path method also identifies if a delay in any step of the project will impact the final project delivery date.

What Is the Critical Path Method?
So, what is the critical path method? Developed in the 1950s by Morgan R. Walker (Dupont) and James E. Kelley Jr. (Remington Rand), the critical path method is a project management tool that captures the critical steps that make up a project, their dependency on other steps, how long it will take to complete each step, and the time it will take to complete all of the steps in the project in its entirety. Once this critical information is defined, you are able to set a project budget.
Wikipedia provides a critical path method definition as: “an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities”. You can think of an algorithm as a set of instructions that must be followed to ensure the success of a project. Algorithms provide a schedule by which each step in a critical path must be achieved. The critical path method experienced its claim to fame initially as it was used on the Manhattan Project in WWII.
A critical piece to understanding the critical path method is that it is designed to determine the longest period of time it will take to complete the critical steps of a project. By identifying the critical steps, you are able to ensure they stay on schedule to avoid delays in project completion.
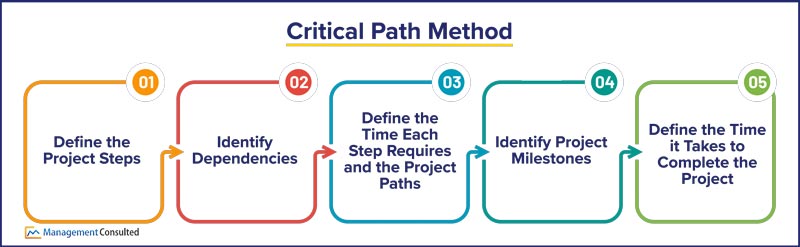
The critical path involves identifying:
- The necessary project steps that must be completed
- The dependencies each step has on each other
- The time each step requires for completion including assigning its sequence in the project
- The milestones of the project
- The total time the project requires for completion
The critical path method also takes into account which important activities need to be completed even if they don’t necessarily have to be done in a specific sequence to achieve project success. The critical path method also defines which project steps have “float”, meaning that they may be delayed without the entire project being delayed.
Critical Path Method Example
In order to see how the critical path method works in action, let’s look at a simple critical path method example. For our purposes let’s look at making the “perfect” cup of espresso - with both your partner and an espresso maker (does anyone else confuse the two?). The following are the key steps that must be taken to ensure success - the creation of a great cup of coffee.
-
Define the Project Steps
In our coffee example, the following key steps must be taken to achieve that perfect cup of coffee:
-
- Purchase the best espresso machine in the business, ensuring it is one that has temperature regulation with sufficient pressure (15 bar)
- Purchase the best burr grinder to sufficiently grind the espresso beans fine enough for extraction
- Purchase the best whole espresso beans with a regulated roasting profile that are within 2 weeks of roasting to ensure freshness
- Purchase the perfect-sized espresso cups
- Use filtered water for the espresso machine
- Warm the coffee extraction head and coffee cups before pulling the shot
- Tamp the coffee grounds perfectly to ensure a consistent extraction and flavor
- Achieve the perfect pressure and temperature when pulling the espresso shot
- Run the espresso machine “pull” for just enough time to achieve the perfect extraction of espresso coffee from the tamped beans
-
Identify Dependencies
Some of these steps are dependent on the others. Some may be done independent of each other. For example, one person may purchase mugs via Amazon on one day and another may purchase the espresso machine on another day from Williams-Sonoma. These are independent steps. Dependent steps include the need for filtered water at the same time as having the espresso beans available to create that perfect cup of espresso.
-
Define the Time Each Step Requires and the Project Paths
In our example it will take time to acquire all of the needed ingredients and tools to make the perfect cup of espresso. There are also separate project paths, one that involves acquiring the tools and ingredients and the other involves actually making the espresso.
Some steps are far more critical than others. In our example, the cup that is used to drink the coffee is far less critical than ensuring the perfect pressure is applied to the ground espresso beans to ensure the best tasting coffee.
There are certain steps that must be accomplished and the time it takes to accomplish them creates the critical path.
-
Identify Project Milestones
In our project, milestones include finding the right espresso machine and acquiring the best tasting beans. Without both of these milestones, you might as well just go to Starbucks.
-
Define the Time it Takes to Complete the Project
In our example, the goal is to determine how long it will take to obtain a liquid in a cup that tastes like it is straight from heaven. This is our critical path.
Critical Path Method Template
There are a myriad of options on the internet that will help jumpstart your own critical path template. Here's just a few:
[globalcta id="CTA-CorpTraining-v1"]
Critical Path Method – Good for Espresso, Better for Project Management
The critical path method is a great project management tool to allow for the prioritization of critical events that must be monitored to ensure the timely completion of a project. It helps identify those steps that are nice to have, but not critical to the delivery of a project if it is delayed.
If you are currently a consultant, or plan to be one, this project management technique is extremely helpful. It manages the many competing project tasks towards completion in a timely manner. The use of this project management tool will allow you to stay on top of many projects at one time and ensure their timely delivery.
Additional Reading:
- Top 7 Business Frameworks to Know
- Utilizing SWOT In A Business Case
- Matrix Management: Benefits, Challenges, & Examples
- The Pyramid Principle