Microeconomics knowledge is highly useful for aspiring consultants. Becoming a consultant is a great way to use your microeconomics skills. As a consultant, you will be paid to help businesses make decisions about pricing, marketing, and other strategic issues. To be successful, you will need to understand microeconomics concepts such as game theory, market structure, and price elasticity. By familiarizing yourself with the basics of economics, you will have a leg up in building trust with clients; they will feel more comfortable following your business recommendations when you demonstrate a strong understanding of microeconomics. In this article, we will explore the most important microeconomic concepts that every aspiring consultant should know. We will also provide some practical microeconomics examples to illustrate how these concepts can be applied in the real world. With this knowledge, you will be well on your way to demonstrating business acumen – both in the case interview and on the job!

Table of Contents
-
- Microeconomics Definition
- Microeconomics vs Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics Examples
- Sustainable Consumption Microeconomics
- Intermediate Microeconomics
- Elasticity Microeconomics
- Game Theory Microeconomics
- Externalities Microeconomics
- Opportunity Cost Microeconomics
- Microeconomics Supply and Demand
- Applied Microeconomics
- Efficiency Microeconomics
- Empiricism Microeconomics
- Margin In Microeconomics
- Equilibrium Microeconomics
- Comparative Advantage Microeconomics
- Cost Curves Microeconomics
- Deadweight Loss Microeconomics
- Graphs For Microeconomics
Microeconomics Definition
What is microeconomics? Microeconomics is all about the study of how people use limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants. In other words, it's the study of how people allocate their time, money, and effort to achieve the maximum satisfaction possible. Microeconomics is a subfield of economics that looks at the behavior of individuals and small groups, such as businesses and consumers. It focuses on what motivates people to make choices and how those choices affect the market.
For example, microeconomics may look at how a business decides what to produce, how much to charge for its products, or how many workers to hire. It can also look at how a family decides what groceries to buy or what type of car to purchase. In general, you can treat this as your microeconomics definition: The decision-making process of firms and households and how these decisions affect the market.
By understanding microeconomic principles, you'll be able to make better decisions in the case interview and make better recommendations to your clients.
Microeconomics vs Macroeconomics
There are two broad categories within the field of economics: microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics focuses on smaller economic units, such as individuals and businesses, while macroeconomics takes a big-picture view of the economy. Both microeconomics and macroeconomics are important for understanding how the economy works, but microeconomics is particularly relevant for consultants.
Microeconomic principles can help consultants understand the behavior of individual economic actors and how they make decisions. This knowledge can be used to advise clients on issues like pricing, marketing, and product development. In addition, microeconomic principles can help consultants understand how to create incentives that encourage people to take desired actions. For example, if a company wants its employees to work harder, microeconomic theory can help identify the type of incentive that would be most effective in achieving this goal.
While macroeconomic principles are also important for consultants, microeconomic principles tend to be more directly relevant to the day-to-day work of consulting. As a result, it’s important to familiarize yourself with microeconomics principles in your journey of becoming a consultant.
Microeconomics Examples
Let’s look at microeconomics examples and the different subsets of microeconomics. We will then demonstrate why each matters to you.
Sustainable Consumption Microeconomics
Sustainable consumption microeconomics is a field of study that focuses on how people can consume responsibly to protect the environment. The goal is to change consumption patterns so that they are sustainable in the long term. Sustainable consumption microeconomics is an emerging area of research, as it can help businesses and organizations reduce their environmental impact.
Intermediate Microeconomics
Intermediate microeconomics is a fascinating field of study that builds on the concepts learned in introductory microeconomics. In Intermediate microeconomics, students learn about more advanced topics such as game theory and information asymmetry. Intermediate microeconomics is also the perfect opportunity to learn about cutting-edge research in the field of economics. Studying intermediate microeconomics as an aspiring consultant is not a necessity but will give you some contextual knowledge that will be helpful to you in your career.
Elasticity Microeconomics
Elasticity is an economic concept that measures how much one thing responds to another. For example, if the price of a product goes up and people continue to buy it at the same rate, then demand is said to be inelastic. On the other hand, if the price of a product goes up and people buy less of it, then demand is said to be elastic. Elasticity can help to explain how pricing and other economic factors impact consumer behavior.
Game Theory Microeconomics
Game Theory Microeconomics is the study of how people interact with each other in certain scenarios based on preferences and payoffs. Game Theory can be used to understand individual strategy behind a wide variety of situations, from chess to the stock market. Game Theory can also help you understand how people make decisions under uncertainty. This is a useful tool for anyone who wants to understand how people interact with each other. In fact, Game Theory was one of the more important tools used to evaluate potential decisions during the Cold War between Russia and the U.S.
Externalities Microeconomics
Externalities are an important concept in microeconomics, and one that is often relevant to consulting work. Put simply, an externality is a cost or benefit that is not experienced by the parties directly involved in a transaction. For example, if a factory produces pollution that harms the health of nearby residents, those residents are said to bear the cost of the pollution (a negative externality). Externalities can be positive or negative, and they can have a significant impact on economic efficiency. As a result, they are often a key area of focus for consultants.
Opportunity Cost Microeconomics
An opportunity cost is often called an indirect cost. It’s the cost of what you are passing up by pursuing any given option and needs to be added to the direct cost of the action you’ve decided to take if you wish to understand the total cost picture. For example, it may cost $100,000 to get an MBA. That’s the tuition. But if you also must stop working one year and forgo a $100,000 salary, the total cost of the MBA is $200,00. $100,000 in direct cost, and $100,000 in lost salary “opportunity cost.”
Opportunity cost microeconomics analysis focuses on the decisions that people make about what to produce, how to produce it, and who will consume it. Opportunity cost microeconomics also looks at how these decisions affect the prices of goods and services in the market. In other words, opportunity cost microeconomics is all about making the best use of your resources to maximize utility!
Microeconomics Supply and Demand
Microeconomics is all about supply and demand. The interaction between these two factors determines the price of a good or service in the marketplace. When demand for a good or service exceeds supply, prices will rise. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices will fall.
Microeconomics is concerned with how these forces interact to determine prices and quantities in specific markets. For the aspiring consultant, understanding microeconomics supply and demand is essential for understanding how businesses operate and how to optimize their performance through better pricing decisions.
Applied Microeconomics
Applied Microeconomics is the study of how people use scarce resources to produce valued goods and services and how these activities interact in markets. Applied Microeconomics is concerned with real-world problems, such as how to design incentives that will encourage people to work hard, how to create marketplaces that are efficient and fair, and how to understand and influence consumer behavior. Applied Microeconomics also has important implications for public policy, as it can help policymakers understand the likely consequences of various policy interventions.
Efficiency Microeconomics
Efficiency Microeconomics is a branch of microeconomics that focuses on the allocation of resources in an economy. Efficiency microeconomics examines how marketplaces work to allocate resources in an efficient manner. Efficiency microeconomics is a critical tool for consultants who advise businesses on how to optimize their operations. By understanding efficiency microeconomics, consultants can help their clients make better decisions about resource allocation, pricing, and production.
Empiricism Microeconomics
Empiricism Microeconomics is the study of how people interact with each other in the market to get what they want. It is a very important subject for those who want to be consultants, as it helps them understand how people think and what they are likely to do in different situations. Empiricist economics spend more time focused on conducting experiments and gathering real-world data, and less time building theoretical mathematical models.
Margin In Microeconomics
Margins are critical for any business to pay attention to. The margin is the difference between the cost of a good or service and the selling price. For businesses, margins are important because they ultimately drive net profitability after taxes. For consumers, margins can impact how much money is available to spend on other goods and services. Margins can also be used to negotiate better prices for goods and services. When considering margin, businesses and consumers are both trying to get the best deal possible. By understanding how margins work, you can be a more effective negotiator and get the best possible price for what you're selling or buying.
Equilibrium Microeconomics
Equilibrium Microeconomics is the study of how market demand and supply affect the prices of goods and services in the market. Equilibrium Microeconomics is based on the principle of supply and demand, which states that the price of a good or service is determined by the interaction between buyers and sellers in the market. Equilibrium Microeconomics is an important tool for aspiring consultants, as it provides them with a deep understanding of how markets operate. Equilibrium Microeconomics is also useful for policy makers, as it can help them to design policies that will achieve their desired outcome in the market.
Comparative Advantage Microeconomics
Comparative advantage occurs when a country, person, or company can produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another entity. In other words, a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good or service if it can produce that good or service more efficiently than another country. Comparative advantage is the basis for international trade, and it is important for consultants to understand how it works. Comparative advantage can help consultants to identify opportunities for their clients to enter new markets and to recommend strategies for expanding their businesses.
When you have a clear comparative advantage, it makes sense to focus more of your time and effort on producing that product. Then, you can trade that product to get the other goods you need. By understanding comparative advantage, consultants can provide valuable insights to their clients and help them to grow their businesses.
Cost Curves Microeconomics
Cost Curves Microeconomics is a tool that enables business professionals to identify and understand the relationships between costs and revenue. The Cost Curves Microeconomics approach consists of four key steps: identifying the Opportunity Cost, constructing the Cost Curve, analyzing the Cost Curve, and making decisions.
The first step, identifying the Opportunity Cost, is essential for understanding the concept of opportunity cost and its impact on business decisions. The second step, constructing the Cost Curve, involves graphing the relationships between costs and revenue. The third step, analyzing the Cost Curve, allows business professionals to identify trends and patterns in the data. The fourth step, making decisions, enables business professionals to make optimal decisions based on their analysis of the Cost Curve data.
Deadweight Loss Microeconomics
Deadweight loss microeconomics can help you understand market inefficiencies. Deadweight loss occurs when there is a discrepancy between what a good or service is worth to consumers and what it costs to produce. This can lead to inefficient allocation of resources, as well as reduced economic activity and growth. Deadweight loss can be caused by several factors, including taxes, subsidies, and price ceilings or floors. As a future consultant, it is important to be aware of this concept and how it can impact the economy. By understanding deadweight loss, you will be better equipped to identify market failures and offer solutions that can help improve economic efficiency.
Graphs For Microeconomics
Graphs for microeconomics are useful visual tools for consultants working with clients. The most popular graph, and the graph used as the basis for a range of other economic analyses, is the price equilibrium graph. It shows how consumers’ willingness to buy more (i.e., demand a higher quantity) as the price decreases (the demand curve) interacts with producers’ interest in making more as the price increases (the supply curve). In the graph below, the expected market price is just over $20, and just under 300 units will be produced and sold at that price.
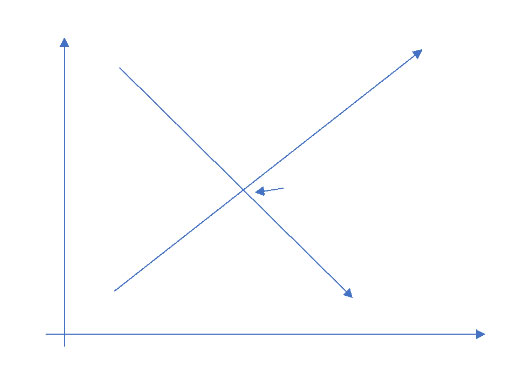
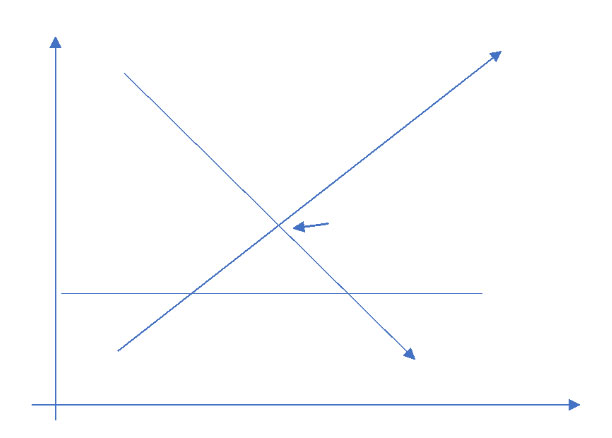
The same framework can be used to understand other specific situations. For example, what happens when a government decides prices can’t go above a certain level? You can model this out using the same framework, and ultimately show that you’ll end with a shortage. That $15 price ceiling will create demand for 350+ units, but producers will probably only make about 150, creating a large shortage.
Conclusion
Microeconomics is a complex and challenging subject, but it is essential to understand for anyone who wants to build a career in consulting. By understanding the various concepts and theories of microeconomics, consultants can develop sound strategies for helping their clients achieve their economic goals. With a solid foundation in microeconomics, the sky's the limit for the ambitious consultant.
Additional Resources:
- Unit Economics: What Is It?
- Circular Economy: What Is It?, Definition, Examples, & Model
- Economic Consulting Case Interview Questions
- Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide